Home![]() books
books
![]() ecology
ecology![]() Latest info
Latest info![]() from space
from space
![]() Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia![]() Animals
Animals![]() Plants
Plants![]() Climat
Climat![]() Research
Research![]() The world beneath Baikal
The world beneath Baikal![]() Geology
Geology![]() Circumbaikal railroad
Circumbaikal railroad![]() Photogallery # 1
Photogallery # 1![]() Photogallery # 2
Photogallery # 2![]() Photogallery # 3
Photogallery # 3![]() Listvyanka
Listvyanka![]() Natives
Natives![]() In German
In German![]() Word of poet
Word of poet![]() Olkhon island
Olkhon island![]() Earthwatch
Earthwatch
![]() Shopping
Shopping![]() Travel agences
Travel agences![]() Guestbook
Guestbook
![]()
Collecton of the articles in Russian
 In 1957, when the public first heard about plans for a cellulose plant at
Baikalsk, people who had mutely obeyed the Soviet government for 40 years
finally howled in protest. Local scientists, writers, fishermen, and ordinary
citizens banded together to fight the plant, igniting an environmental movement
that was a direct forebear of all Soviet activism to come. Their protests
were mostly ignored. Yet at a time in the Soviet Union when the fires of free
speech were being stamped out wherever they appeared, a small flicker burned
fiercely in the Siberian wilderness.
In 1957, when the public first heard about plans for a cellulose plant at
Baikalsk, people who had mutely obeyed the Soviet government for 40 years
finally howled in protest. Local scientists, writers, fishermen, and ordinary
citizens banded together to fight the plant, igniting an environmental movement
that was a direct forebear of all Soviet activism to come. Their protests
were mostly ignored. Yet at a time in the Soviet Union when the fires of free
speech were being stamped out wherever they appeared, a small flicker burned
fiercely in the Siberian wilderness.
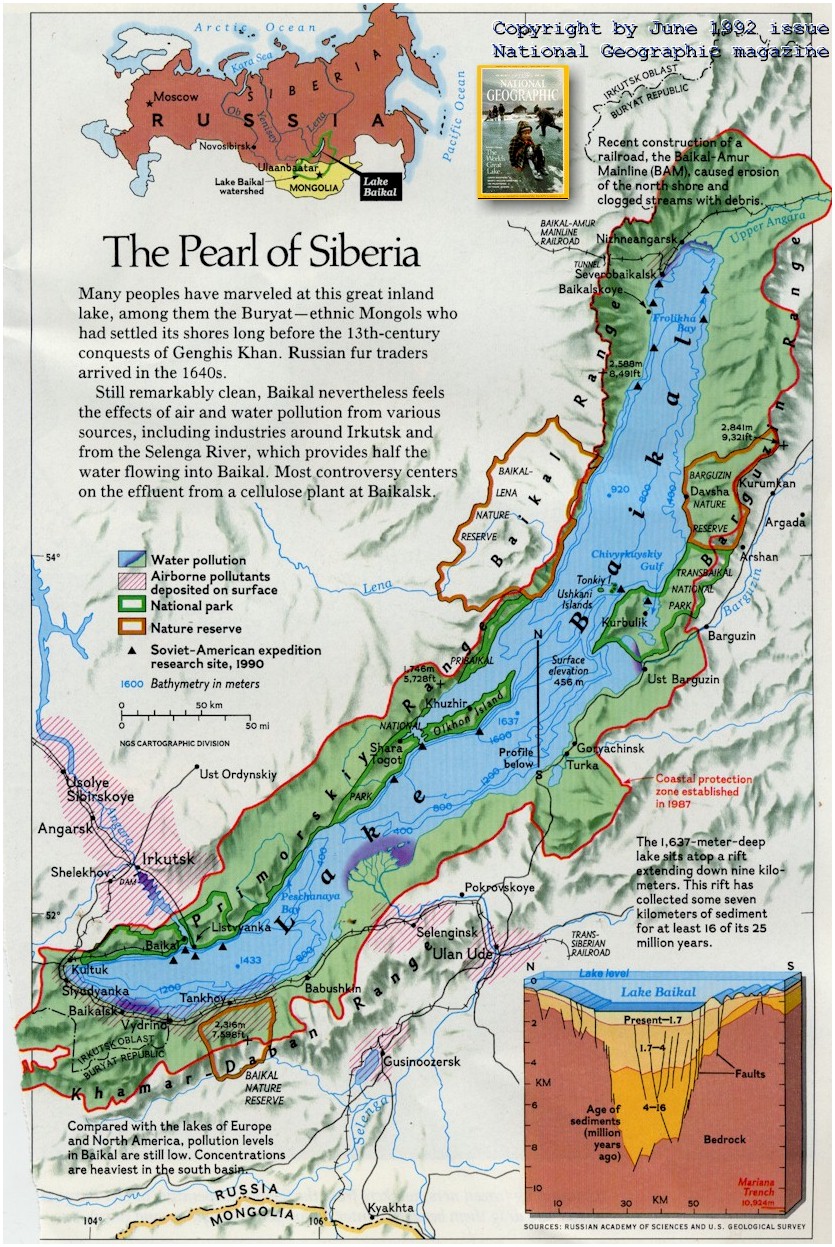
After years of protest, the lake's defender were rewarded in April, 1987, when the Soviet government issued a comprehensive decree protecting Lake Baikal. Among other things, it abolished logging anywhere close to the lake shore and decreed that the cellulose plant be "reprofiled" for activities harmless to the environment by 1993. Exactly what those activities might be has not been decided.
 Meanwhile the
dumping of industrial waste into Baikal continues, and bilious smoke still
rises from the plant 24 hours a day.
Meanwhile the
dumping of industrial waste into Baikal continues, and bilious smoke still
rises from the plant 24 hours a day.
For over 30 years this very iussue has been the centerpiece of discussions and arguments between scientists, environmentalists, developers, industrialists and governmental officials. The environmentalists lost the battle to stop construction of this huge factory on the shores of Baikal in the 1960's. Since then, there have been various efforts to use common sense and find an alternative to the existence of the Pulp and Paper Plant at the southernmost point of Baikal. Some of these efforts have been more obvious, but mostly they have consisted of "routine" work by researchers, scientists, and those who cared.
Dozens of international expeditions that worked on Baikal during recent years have come to the unanimous opinion: Baikal remains the cleanest reserve of fresh water, but the local alterations in its ecosystem near the Baikal pulp-and-paper plant and the region where the Selenga River flows into Baikal, impose their negative effects on its inhabitants.
The intensive exploitation of the Baikal Territory adversely affects the primordial, easily injured Siberian nature. We haven't yet learnt to live in harmony with it, and the way to this seems to be long.
Home![]() Books
Books ![]() Ecology
Ecology![]() Latest
info
Latest
info
![]() from
space
from
space ![]() Encyclopedia
Encyclopedia
![]() Animals
Animals![]() Plants
Plants![]() Climat
Climat![]() Research
Research![]() The world beneath Baikal
The world beneath Baikal![]() Geology
Geology![]() Circumbaikal railroad
Circumbaikal railroad![]() Photogallery # 1
Photogallery # 1![]() Photogallery # 2
Photogallery # 2![]() Photogallery # 3
Photogallery # 3![]() Listvyanka
Listvyanka![]() Natives
Natives![]() In German
In German![]() Word of poet
Word of poet![]() Olkhon island
Olkhon island
![]() Earthwatch
Earthwatch
![]() Shopping
Shopping![]() Travel agences
Travel agences![]() Guestbook
Guestbook
realvideo
![]() Transsiberian
railway.
Transsiberian
railway.![]() Inside
the train at Transsiberian railway,download .mov 468kb
Inside
the train at Transsiberian railway,download .mov 468kb![]() Circumbaikal
railway
Circumbaikal
railway![]() Lake
Baikal beauty
Lake
Baikal beauty![]() Yachts
at Baikal
Yachts
at Baikal![]() Brown
bears at lake Baikal shores in spring
Brown
bears at lake Baikal shores in spring![]() Aqualangist
under Baikal ice
Aqualangist
under Baikal ice![]() At
lake Baikal beneath
At
lake Baikal beneath![]() Baikal
nerpas
Baikal
nerpas![]() History
of Trans-Siberian
railway
History
of Trans-Siberian
railway
![]()
|
|
|